This is a topic of great interest to me, I believe that it is important for the future welfare of the world population.
Below is an excerpt of the introduction to a paper I wrote on it this year:
A transgenic organism is one that has artificially or naturally introduced DNA from another organism introduced into the germ line. This is a type of genetic engineering whereby an organism is produced on the basis of desired phenotypes by selectively breeding the associated genotypes or by introducing suitable genotypes from other organisms.
Scientists working on Blight-resistant potatoes want to produce it as one of the world’s first major and widely grown foods that has incorporated defences for plant diseases genetically engineered into its genome. Plant diseases are a major problem as they ruin around 20% of the world harvest annually. In 2050, it is expected that the human global population will boom to more than 9 billion people, and the demand for food could rise between 70% and 100%.There will be little arable land left as the population expands, let alone have enough food to feed billions and that survives diseases and pests.
Not only will an increase in population mean that there will be less space, but also climate change produces increasingly difficult circumstances where crops cannot be grown, for example global temperatures increasing.
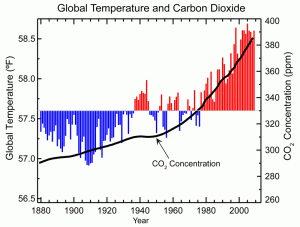
There is a definite increase in this graph showing that global surface temperature is rising the increase is around 1.4 °F since the early 1900s. This rise in temperature means that some crops will not be able to grow in their usual locations, or will fail to produce a high enough yield for consumers before insect or disease infestations accumulate at hotter temperatures.
Climate change has also drastically affected drought and flooding levels which are both on the increase, making the weather extremely unpredictable and difficult to grow in. Normally, farmers would selectively breed crops with characteristics that are better for that area’s temperature and rainfall measurements, however, the sudden changes in weather mean that this has become extremely difficult.
Whilst the rise in CO2 concentration could be considered a positive aspect for a plant as it is often the limiting factor on photosynthesis, it has been found that an elevated level of CO2 can be too much for plants and stomatal numbers decrease as they develop and they close meaning that transpiration is lowered and growth can slow down, there is a compensation point that needs to be maintained. Accordingly, there is a need for a plant that can cope with drastic weather changes and still produce a high yield for the ever growing population on the decreased arable land. All these factors and resistance to pests and diseases are possible through fine tuning different types of genetic engineering.
